主要栏目
kubernetes
更多 >>-
第三章、围绕 kubernetes 相关生态
2022-05-05
-
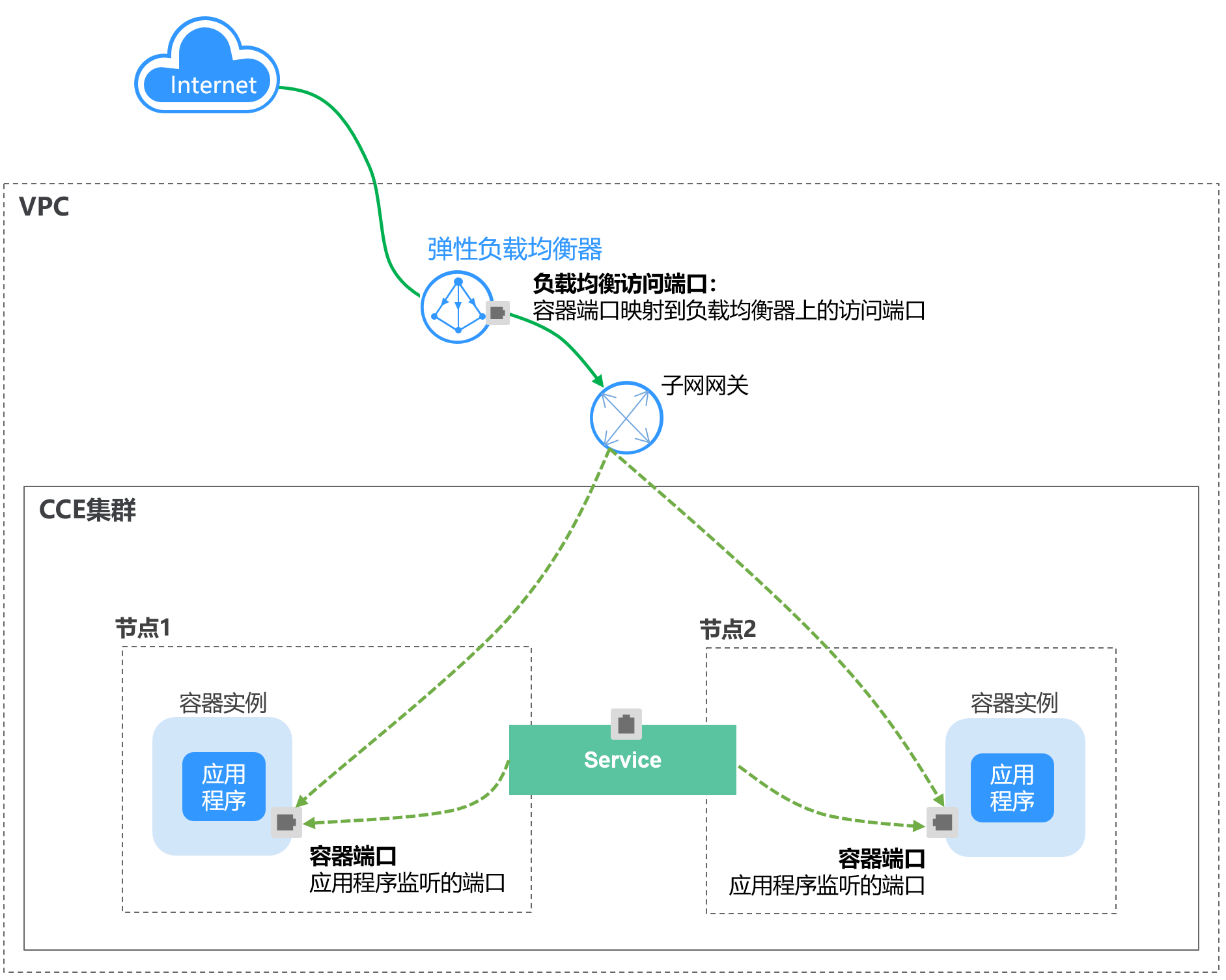
第二章、kubernetes 基础要点梳理
2022-05-05
-
第一章、容器化的实现原理
2022-03-14
-
kubeconfig 合并工具-kubecm
2022-02-10
-
kubebuilder & code-generator(四)
2021-12-15
devops
更多 >>-
本地网络与云厂商 vpc 网络一体化方案
2022-09-12
-
git 更新代码慢原因分析
2022-08-15
-
Sonar 复杂度指标
2022-07-18
-
云原生企业网络规划-真实案例
2022-05-25
-
云原生自运维平台的设计
2022-05-24
container
更多 >>-
Docker 存储驱动
2022-03-15
-
docker 架构简要
2022-03-03
golang
更多 >>-
kubectl 源码概览
2022-12-16
-
golang 结构体断言
2022-03-25
-
golang下划线(_)的三种用法
2021-12-07